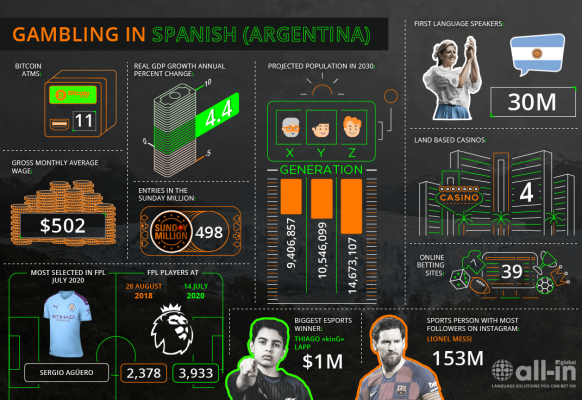
Thu Jul 30th / Marina
MEXICAN CULTURE INSIDE A GAME: “LA LOTERIA MEXICANA”
Here are All-in Global’s three best tips when localizing iGaming content for the rapidly growing Mexican market:
- Play “La Loteria Mexicana” to get a crash course in Mexican gaming culture.
- Hire native Mexican Spanish translators.
- Make sure the translators understand iGaming terminology.
If you’re looking to localize your iGaming content for the Mexican market, it’s important to note that connecting with Mexican players will require more than simply translating your content into Spanish. Although this country has an impressive number of Spanish speakers (roughly 121.9M – source: statista), localization is the key step that will make you sound like a local.

A great localization job will help you build trust and loyalty among your audience and consequently more engagement. At All-in Global we are specialists in localizing iGaming content and we only hire native-speaking professionals with a vast knowledge of iGaming lingo. This means they will “speak” to your leads in a language they can relate to.
We’ve collected multiple interesting aspects of Mexican culture by analyzing the traditional game “La Loteria Mexicana.” This information allows you to find unique details that attract a specific target and help to create meaningful connections with your brand.
Want to try La Lotteria Mexicana for yourself?
You can download it on Google Play here and in the App Store here.
THE ORIGINS OF LA LOTERIA MEXICANA
The history of this massively-popular game began in the 1400s in Italy while arriving in Mexico in 1769. It began as a game that was played by the upper-class but became popular at Mexican fairs when soldiers who returned from the Mexican War of Independence (1810-1820) helped make a favorite hobby become a popular game throughout the population.
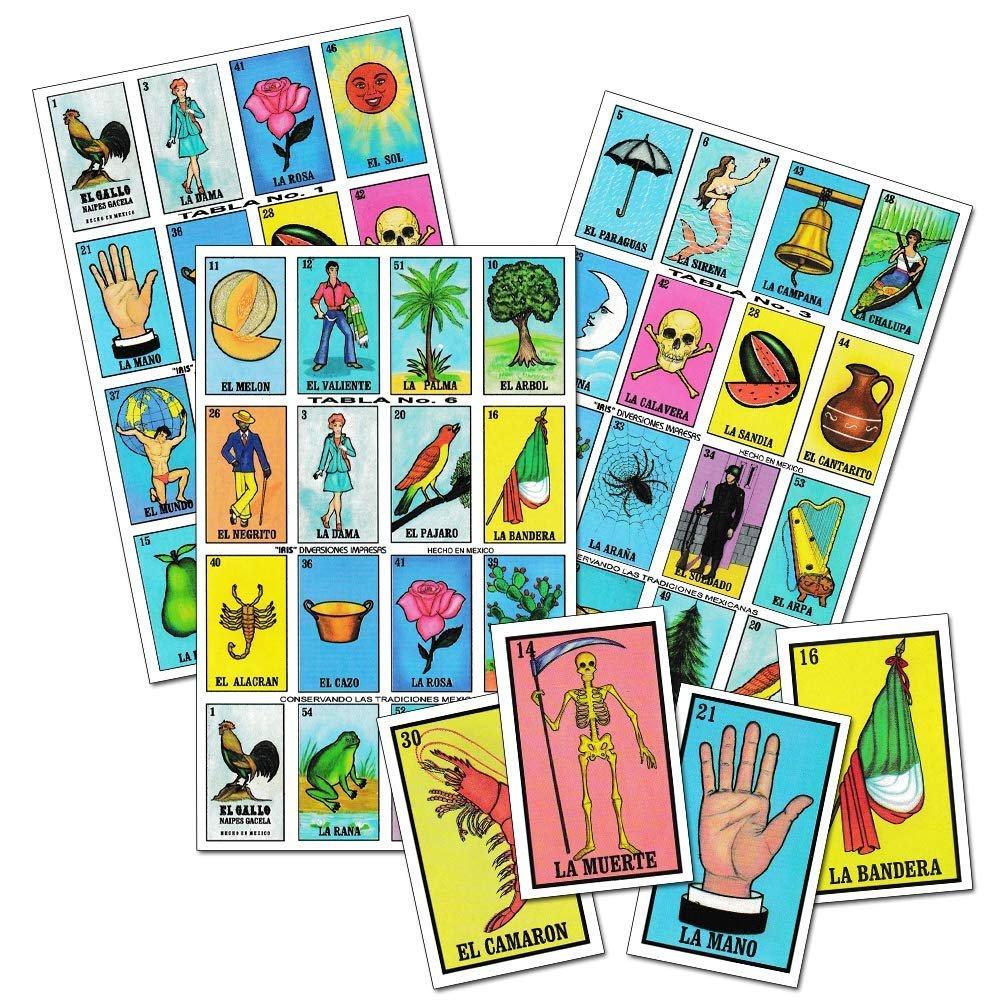
Because the rules of La Loteria Mexicana are so similar to American bingo this game is also known by many as “Mexican Bingo.” The major difference between the two games is that American bingo is based only on numbers while Mexican Bingo has a set of 54 illustrated cards and boards with randomly selected images that match the illustrated cards. There are some variations on the rules to play this game but generally, the first player completing a horizontal or vertical row shouts “¡Loteria!” and wins the game.

The iconic illustrations in this game were introduced in Mexico in 1887 by French businessman Don Clemente Jacques. He standardized the illustrations when beginning mass printing so he could give this game as a gift when selling boxes of canned food for the soldiers.
THE ICONIC ILLUSTRATIONS OF MEXICAN CULTURE
Here are some of the 54 illustrations of Mexican Bingo that can introduce you to its Mexican roots and inspire your brand to create and adapt content to this promising market.
El gallo
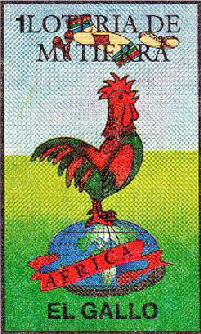
In the Mexican culture, el gallo (roosters) represents strength. It is also a symbol of the popular cockfighting (Palenque) where two roosters fight in a ring. It is a very popular and traditional form of entertainment all over Mexico. Some campaigns against animal cruelty resulted in the prohibition of these events in several Mexican states.
El Bandolón

Mexico is known as a place of “fiesta”. In fact, music represents a big part of Mexican identity and they have classical styles that have become extremely popular such as Mariachi. Bandolón is a musical instrument with six strings, distinguished to be part of all the “fiesta” popular songs.
El Cazo

It’s a cooking cylindrical container, wider than it is tall used to cook the popular carnitas de puerco ( Mexican pork carnitas). This is also the origin of the famous “cazueladas,” which represents a big part of Mexican gastronomy.
La Chalupa

Represents a type of small boat that can be used as a shallop or water taxi. These boats are typically used as floating stands for vendors to attract tourists.
WHY IT’S SO IMPORTANT TO LOCALIZE YOUR CONTENT TO MEXICAN SPANISH?
The Spanish which is spoken in Mexico has a distinct set of influences from the Spanish spoken in Europe which results in a specific dialect in terms of vocabulary and grammar that is unique to the country. It’s important to clarify that European Spanish and Mexican Spanish are not distinct languages but different dialects of the same language. People from both countries are able to understand the majority of communication from both dialects but some particular differences will make them feel confused. if you want the full acceptance of your product, you’ll want to avoid these feelings of unfamiliarity among your players. At All-in Global we strongly suggest that you take a safe-bet by hiring professional native-speakers to craft these details for you.
Here’s a list of some major differences between European Spanish and Mexican Spanish:
-The pronunciation
In European Spanish, there’s a clear differentiation when pronouncing the letters “S”,”C” and “Z,” while in Mexican Spanish they generally sound the same.
It’s also commonly said that the European Spanish tends to sound a bit more guttural since it has Arabic influences. The last point would be extremely relevant if you were looking for a voice-over to communicate with your audience. The pronunciation of European Spanish can sound a bit “rude” in the ears of a Mexican and it’s a near-certainty that you wouldn’t want to take that risk with your audience.
-The grammar
One of the biggest differences between these two dialects is in the use of the term “vosotros” and “ustedes”. While in European Spanish they differentiate the second-person of the plural in an informal version – vosotros – and in a formal version – ustedes. In Mexico, they only use “ustedes”, meaning that the verb conjugations will also be distinct.
-The vocabulary
There is some distinct vocabulary used in both dialects that may cause some unfamiliarity when communicating with these specific targets. The list is long but here are some examples:
English: Computer
European Spanish: Ordenador
Mexican Spanish: Computadora
English: Cell phone
European Spanish: Móvil
Mexican Spanish: Celular
English: Golf course
European Spanish: Campo de golf
Mexican Spanish: Cancha de golf
English: To take
European Spanish: Coger (The verb coger has a sexual connotation in LatAm countries)
Mexican Spanish: Tomar
English: Press (in video games)
European Spanish: pulsar
Mexican Spanish: oprimir (this word would mean oppress in European Spanish)
As you can see, these two Spanish dialects have some differences that can’t be ignored when your goal is to successfully engage with your target audience. Carefully crafting and delivering the right message can dictate the difference between building trust or building a bad reputation for your brand.
As a language service provider dedicated to the gaming industry, we know that the process of localizing your iGaming content into the correct Spanish variant can be complex and we highly recommend that you involve professional native-speaking translators and copywriters in the process as early as possible. Each LatAm market is unique and might require a different Spanish variant. The same differences happen between the Brazilan Portuguese and European Portuguese, where the same variant does not suit both markets.
If you are interested in getting to know more about the LatAm iGaming market we invite you to explore our iGaming infographics. We would love to hear about your LatAm localization project and help you to create content that builds a strong connection with your players. Contact us: [email protected]
Links:
Spanish (Mexico)
Spanish (Argentina)
Spanish (Chile)
Spanish ( Columbia)
Spanish (Peru)
Spanish (Venezuela)
Portuguese (Brazil)